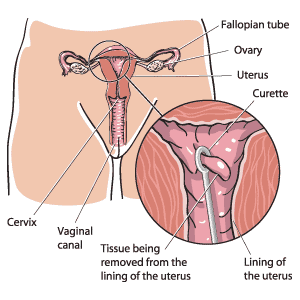
Description of the procedure
In a dilation and curettage (D&C), the lining of the uterus is removed. Doctors may use this procedure to:
- take samples of tissue from the uterus to determine if an abnormality exists
- remove endometrial polyps
- remove tissue that is left in the uterus after an incomplete miscarriage (a miscarriage where some tissue is left in the uterus), an incomplete abortion (a situation where tissue is left in the uterus after an abortion), or childbirth
- perform an abortion (during the first 12 to 15 weeks of pregnancy)
This procedure is usually performed in a hospital or clinic. Most women go home the same day or the next day.
When should this procedure be performed?
You and your doctor will decide when this procedure is required.
Why is this procedure performed?
This procedure allows doctors to detect problems with the uterine lining, rule out cancer, and help improve menstrual periods of women with heavier than normal menstrual flow. This procedure removes tissue that has remained in the uterus after childbirth or an incomplete miscarriage or abortion. It may also be used to perform an abortion during the first 12 to 15 weeks of pregnancy.
Are there any risks and precautions?
Certain risks are common to all surgery and anesthesia. These risks depend on many factors including the type of surgery and your own medical condition. The possible, but very rare, side effects include: side effects of the anesthetic, breathing problems, infection, bleeding, scarring, and death.
Although D&C is generally considered safe, it does have some risk of side effects or complications. These include:
- damaging the uterus or cervix, which may make pregnancy more difficult (this is more common for people who have repeated D&Cs)
- tearing or puncturing the uterus, bowel, or bladder
Speak to your doctor immediately if you experience any of these signs of infection requiring medical attention:
- fever
- foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- heavy bleeding (filling more than three sanitary pads in a few hours)
- severe cramps
If you are concerned about any symptoms following this procedure, speak to your doctor. Take the time to be sure you understand all the risks of complications and side effects as well as any precautions you or your doctor can take to avoid them. Be sure your doctor understands all your concerns.
What happens during the procedure?
Either a general or a local anesthetic may be used. If general anesthesia is used, you will not be awake for the procedure. If a local anesthetic is used, the area will be numb but you will be awake.
- The doctor places an instrument called a speculum into the vagina to hold the vaginal walls open and allow a better view of the cervix.
- Metal dilators gradually stretch the cervix open and tissue is gently scraped from the inside walls of the uterus using an instrument called a curette.
- Tissue may be suctioned from the uterus using a vacuum pump. Samples of tissue from the uterine lining are sent to a laboratory for analysis, if necessary.
This procedure usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes.
How should I prepare for this procedure?
Before having this procedure, discuss the advantages, disadvantages, long-term risks and consequences associated with the procedure with your doctor. Be sure you fully understand what will happen and are comfortable with your doctor's answers to your questions.
In certain situations, your doctor may need to dilate your cervix more than the usual D&C. If this is the case, your doctor may want you to start dilating your cervix a few hours to a day before the procedure, either by giving you medication that softens the cervix or by inserting a slim rod into your cervix that helps expand the cervix by absorbing fluid from your cervix.
Do not eat for 8 hours before the procedure. You may continue to drink clear liquids until 2 hours before the procedure. If your doctor has recommended different times, follow the timing recommended by your doctor.
Tell your doctor about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have. Driving is not recommended for the first 24 hours after the procedure so arrange for someone to drive you from the hospital or clinic.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the procedure.
What can I expect after the procedure?
After this procedure, you will likely feel these normal side effects:
- irregular vaginal bleeding for the first couple of weeks - use sanitary pads instead of tampons
- pain and cramping for a few days - your doctor will likely prescribe pain medication
It is important to rest to help you recover. You can return to your normal activities when you feel better, usually within a day or so.
Avoid douching or using tampons for the first few weeks after the procedure.
Sexual intercourse is not recommended for 2 weeks (or longer, as recommended by your doctor) to avoid infection and to help the uterus heal. Women who are still having periods may find that their next period comes earlier or later than usual.
Results
If you have had the procedure to check for abnormalities of the uterine lining, ask your doctor when your test results should be available.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Dilation-and-Curettage