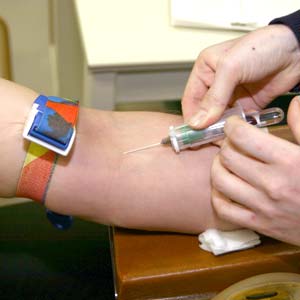
Description of the test
Blood is made up of many different components. A complete blood count (CBC) test involves taking a sample of your blood from your body and looking at the size, shape, numbers of cells in the blood, as well as other characteristics of the blood.
A CBC test looks at the:
- number of red blood cells
- number of white blood cells
- numbers of each white blood cell type
- number of platelets
- volume of red blood cells in the blood (also called hematocrit)
- amount of hemoglobin (carries oxygen to cells)
- size and shape of the cells (abnormal cells may indicate an infection or conditions such as anemia)
- other measurements related to red blood cells
How often should the test be performed?
The frequency of this test is determined by your doctor. More frequent testing may be recommended if you have medical conditions such as anemia, malaria, hemophilia, or certain types of cancer.
Why is this test performed?
Doctors often request this test to get a better understanding of a person's overall health. Results from this test may provide valuable clues if the person is experiencing signs of fatigue or sluggishness, which are often related to anemia.
The test can also help diagnose or monitor certain conditions such as leukemia, bleeding disorders, infection (e.g., bacterial infections, appendicitis, viral infections, malaria), and to evaluate the body's response to certain medications.
Your doctor may also request that you have a CBC test done if you are taking medications that can affect your blood cell counts.
Are there any risks and precautions?
There is very low risk of side effects with this test. Some people experience slight bruising or tenderness where the needle enters the vein.
The test may have a risk of infection (if the area is not properly sterilized before the sample is taken), bleeding from where the needle was inserted, or bruising around the area where the needle was inserted.
The vein where the needle is inserted may become swollen in rare cases. A warm compress can be used a few times per day to treat this.
People with bleeding disorders or anyone taking medication that reduces the ability of the blood to clot (e.g., warfarin, ASA, or other anticoagulants) should tell the technician before the samples of blood are taken. These conditions and medications may require special attention at the time of testing.
If you are concerned about any symptoms following this test, speak to your doctor. Take the time to be sure you understand all the risks of complications and side effects as well as any precautions you or your doctor can take to avoid them. Be sure your doctor understands all your concerns.
What happens during the test?
Blood is collected into one or more small vials labelled with your information.
The technician should wear fresh latex gloves and use a new, single-use needle for each procedure.
- A technician or nurse wraps a wide elastic band around your upper arm to help locate the vein.
- Once the vein is located, usually on the inside of your elbow, the area is disinfected using alcohol swabs.
- The technician inserts a needle into a vein and pushes a vial onto the needle to collect the blood.
- The elastic band is removed and after the blood is collected, the needle is removed and discarded.
- You will have to hold a small piece of cotton over the area until bleeding stops. A small bandage will be applied to hold the cotton in place.
The test is almost painless for most people, although feeling a slight pinch when the needle is inserted is normal. The vials of blood are then sent to a laboratory to be tested.
How should I prepare for this test?
In most cases, you do not need to do anything to prepare for this test. However, if you are having other blood tests at the same time, you may need to fast (not eat or drink) before the test. Follow the instructions provided by your doctor or health care professional. Wearing clothing with no sleeves or loose sleeves is recommended so that your upper arm can be exposed.
Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the test.
What can I expect after the test?
Slight tenderness may occur where the needle was inserted. Keep pressure on the area after the needle is removed to prevent bruising.
Results
The laboratory will send a report to your doctor with all the test results. Ask your doctor when your test results should be available if you want to discuss the results with him or her.
The result of each individual test is given as a number. Since the CBC measures a variety of different things, your results will contain many different numbers. Each result should fall within a certain range. If your results are outside this range, your doctor may or may not recommend other tests or treatments.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Complete-Blood-Count