Description of the test
A Pap smear (also known as a Pap test) is useful in detecting, preventing, and treating cervical cancer. A Pap smear allows for the early detection of abnormal cells on the cervix - cells that may develop into cancer in the future. Cells are examined with a microscope in order to see any abnormalities.
Pap tests are usually done at the doctor's office. Sometimes a nurse is present to observe or assist with the test. If you would like a nurse present, let your doctor know before the test begins.
How often should the test be performed?
Your doctor will recommend when and how often this test should be done. Although the specific age recommendations can vary, most experts recommend that all women who have been sexually active should have regular Pap tests by the time they’re 21 and should have this test done every 1 to 3 years. Talk to your doctor about when and how often you should have a Pap smear.
If you are older than 70 years of age, talk to your doctor about whether you need to continue having Pap smears.
Why is this test performed?
Pap tests check for changes and abnormalities in the cervical cells, which may indicate that the cells may later develop into cervical cancer. Checking for these signs on a regular basis makes it possible for early detection and early treatment of problems.
Are there any risks and precautions?
As a precaution, tell your doctor (or health care professional performing the test) if you have any allergies to latex as they may use latex gloves during the test.
You should also tell them if you are or may be pregnant, if you have ever had an abnormal pap smear result, and if you are taking any medications.
What happens during the test?
You may feel nervous before the test. If so, take a few deep breaths to help relax. Before the test, you need to undress and put on a paper gown. Store your belongings safely or take important items into the room with you.
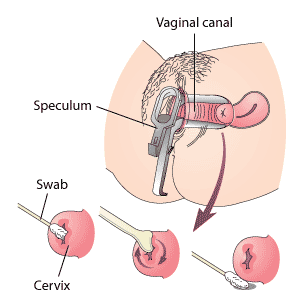
Your doctor or the health care professional performing the test (such as a nurse practitioner) will ask you to lie on an examination table with your feet in stirrups. The doctor will likely ask you to move further down the table, then part of the table folds downwards to allow the doctor to reach you more easily.
The doctor will carefully insert a speculum (a sterile instrument that helps keep the vagina open) for clearer view of the cervix. The speculum is usually lubricated with a sterile lubricant to make insertion easier. The doctor will remove cells from the cervix with a swab, wooden spatula, or brush. The sample is placed in a container and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Samples of bacteria found in the vagina may also be taken at this time.
The test may cause some slight discomfort as the cells are removed. Also, if the speculum is not warm, it may feel somewhat uncomfortable. Make sure to tell the doctor if you feel pain or severe discomfort during the test.
How should I prepare for this test?
Test results are most accurate when you:
- schedule the test for a time when you do not have your menstrual period. For best results, the test should be done in the middle of your cycle (approximately 10 – 20 days after the first day of your previous period)
- do not douche, take a bath, or use any vaginal products such as creams, sprays, or tampons for at least 48 hours before the test
- avoid sexual activity for 1 to 2 days before the test
Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the test.
What can I expect after the test?
You may need to remove excess lubricant after the test with paper towels. Some women experience mild bleeding after the test for 1 to 2 days.
After the test, you may resume your normal activities.
Results
Your doctor receives results of the test a few days or weeks later. The results will indicate if any abnormalities were found. Abnormal cells may be different in size or shape, or may vary in other ways. If these cells are found, you may have to undergo additional tests to determine the cause of the abnormal result.
Your doctor will review the bacterial analysis as well. Certain bacteria and viruses cause sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Your doctor will be able to tell you if any infection was found.
If treatment is needed, your doctor will consider your test results, age, and medical history when recommending a treatment option.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Pap-Smear