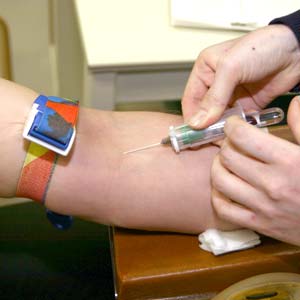
Description of the test
The thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is made by the pituitary gland and it signals the thyroid gland to make hormones that regulate your metabolism (how your body uses energy).
The TSH test measures how much TSH you have in your blood to determine if you have any problems with your thyroid gland.
How often should the test be performed?
You may be required to have this test regularly if you have a problem with your thyroid or are taking thyroid medication. If you do not have any underlying thyroid conditions, then your doctor may order this test periodically to make sure your thyroid is working properly. If you have symptoms of thyroid problems (e.g., changes in weight, heartbeat, body temperature, and muscle function), you may need a TSH test to determine the cause. Ask your doctor about whether or not you require a TSH test.
Why is this test performed?
Hyperthyroidism occurs when your thyroid is making higher than normal levels of hormones, which can result in weight loss, a rapid heart rate, nervousness, and a feeling of being too hot. Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid is making lower than normal levels of hormones, which can result in weight gain, tiredness, constipation, and a feeling of being too cold.
The TSH test is used to check for these thyroid problems and can also help determine why the thyroid gland is not working properly. For people who are on thyroid medication or have had other treatment for their thyroid (e.g., surgery or radiation), the test can be used to monitor thyroid function.
Are there any risks and precautions?
There are no major risks associated with this test. The prick of the needle may hurt slightly when your blood sample is taken. The site on your arm where the blood sample is taken may become bruised or sore for a little while after the test.
What happens during the test?
A blood sample will be taken via a small needle that is inserted into a vein in your arm. An elastic band (tourniquet) may be wrapped around your upper arm to make your veins larger so it is easier to insert the needle. Your blood will be collected through the needle into an attached vial. You will be given some gauze or a cotton ball to hold over the site where the needle was inserted and told to apply slight pressure to stop any bleeding. This process only takes a few minutes.
How should I prepare for this test?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have. You should also tell your doctor if you have had exposure to radioactive materials or X-rays that used iodine dye recently or if you are severely stressed, as all these could affect your test results.
What can I expect after the test?
Your blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for testing. You will be able to return to your normal activities immediately after the test.
Results
TSH levels are measured in milli-international units per litre (mIU/L) or milliunits per litre (mU/L). Ask your doctor whether your TSH levels are high, normal, or low.
Higher levels may indicate an underactive thyroid, a pituitary gland tumour, or not enough thyroid medication. Lower levels may indicate an overactive thyroid, pituitary gland damage, or too much thyroid medication.
Your doctor will tell you whether your results are considered normal or abnormal for your particular situation and schedule further testing if needed.
Ask your doctor when your test results will become available.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Thyroid-stimulating-Hormone-Test