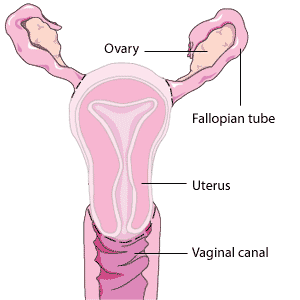
Description of the procedure
A hysterectomy is surgery that is performed to remove a woman's uterus. There are several different types of hysterectomy, including:
- subtotal hysterectomy, where the uterus is removed but the cervix is not
- total hysterectomy, where both the uterus and the cervix are removed
- total hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy, where the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and Fallopian tubes are removed
- radical hysterectomy, where the uterus, cervix, and nearby lymph nodes are removed
Doctors usually perform this procedure under anesthesia in a hospital setting.
When should this procedure be performed?
Doctors perform this procedure only when it is medically necessary. After this procedure, a woman cannot become pregnant.
Why is this procedure performed?
A hysterectomy may be performed to treat a variety of gynecological conditions, including:
- cancer of the cervix
- cancer of the uterus
- cancer of the ovaries
- endometriosis (a condition where parts of the uterus lining end up in other areas of the body, usually in the ovaries, fallopian tubes or pelvic area, causing pain)
- heavy bleeding (which may occur after childbirth) that other treatments do not control
- pain in the pelvis that does not go away with treatment
- uterine fibroids (non-cancerous tumours in the uterus)
- weakening of the uterus ligaments which hold the uterus in place (uterine prolapse)
Are there any risks and precautions?
Certain risks are common to all surgery and anesthesia. These risks depend on many factors including the type of surgery and your own medical condition. The possible, but very rare, side effects include: side effects of the anesthetic, breathing problems, infection, bleeding, scarring, and death.
Although a hysterectomy is generally considered safe, it does have some risk of side effects or complications. These include:
- blood clots
- damage to nearby organs, such as the bladder, rectum, and urinary tract
- damage to the ovaries, which could lead to decreased levels of certain hormones
- early menopause, if the ovaries are removed or if they lose their ability to function
- excessive bleeding
- pain during sexual intercourse
- reactions to the anesthetic
- serious infections
- urinary problems
If you experience these side effects or complications, contact your doctor immediately.
If you are concerned about any symptoms following this procedure, speak to your doctor. Take the time to be sure you understand all the risks of complications and side effects as well as any precautions you or your doctor can take to avoid them. Be sure your doctor understands all your concerns.
What happens during the procedure?
A hysterectomy is done under general anesthesia so you will not be awake during the procedure. In some cases doctors may use an epidural (an anesthetic in the spine) to numb the surgical area instead of putting you to sleep with general anesthesia.
If the uterus is to be removed abdominally, doctors begin the procedure by making an incision in the lower abdomen. Vaginal removal requires no incision in the abdomen. A cut is made in the vagina to allow the removal of the uterus.
The procedure takes approximately 1 to 3 hours.
How should I prepare for this procedure?
Before having this procedure, discuss the advantages, disadvantages, long-term risks, and consequences associated with the procedure with your doctor. Be sure you fully understand what will happen and are comfortable with your doctor's answers to your questions.
Before the procedure, doctors request a number of tests that provide a clearer picture of your uterus and ovaries. A pelvic exam, Pap test, and pelvic ultrasound are usually requested.
Do not eat for 8 hours before the procedure. You may be able to continue to drink clear liquids until 2 hours before the procedure. If your doctor has recommended different times, follow the timing recommended by your doctor.
Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have. Arrange for someone to drive you home from the hospital.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the procedure.
What can I expect after the procedure?
The standard procedure following surgery with general anesthetic will be followed.
- Immediately after surgery, you will be brought to the hospital's recovery room until the anesthetic wears off. Nurses will be available if you need help. You will likely feel groggy, sore, and possible nauseated.
- After you have recovered from the anesthetic you will be transferred to a hospital ward for the rest of your hospital stay, if you are staying over night. If you are not staying over night, you will be discharged from the hospital and allowed to go home. After the surgery you may be given medication for pain and infection prevention.
- Before you go home, the doctor or nurse will go over what you need to do at home to complete your recovery.
Spending one or two nights at the hospital is common for most women.
It is common for a doctor to recommend a pain medication to control any discomfort after this procedure. Your doctor will likely recommend this for you. Resting afterwards will help speed the healing process, although you may need to take time off of work or cancel your regular activities until you recover. It usually takes 4 to 6 weeks to heal from a hysterectomy.
Sanitary pads should be used for any bleeding and discharge that you experience. This may continue for up to several weeks after surgery. Speak to your doctor immediately if you experience fever, severe bleeding, cramps, or foul smelling discharge.
Sexual intercourse is not recommended for approximately 6 weeks to avoid infection and to help the area heal. You should also avoid heavy lifting or any other strenuous activity.
If you were having menstrual periods before the surgery, you will no longer have them after the surgery.
Results
Results will depend on the reason for the hysterectomy. Hysterectomy can be lifesaving when performed to control heavy bleeding from the uterus. It can be an effective treatment for gynecological cancers. It can also relieve the symptoms of fibroids, endometriosis, and other chronic pelvic pain problems.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Hysterectomy