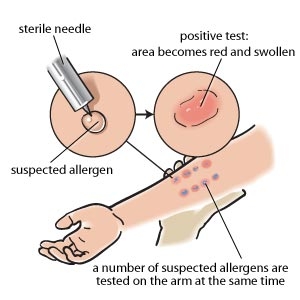
Description of the test
An allergy skin test identifies which substance triggers an allergic reaction. A small amount of the substance, or allergen, is introduced to the body through the skin. If the skin reddens or swells, then the test is read as positive and the person is probably allergic to that substance.
The reaction is due to the release of histamine, a chemical naturally found in the body that causes swelling, redness, and itching (also known as a wheal). This test is usually performed or supervised by an allergist.
How often should the test be performed?
Your doctor will recommend when and how frequently this test is required.
Why is this test performed?
Allergy skin tests are performed to identify what allergen is causing allergy symptoms (such as sneezing, nasal congestion, itchy eyes, wheezing, skin rash, and swelling) so that people can avoid the trigger if necessary and plan appropriate treatment with their doctor.
There are many allergens, including foods, medications, environmental substances (such as ragweed and fungus), as well as contact allergens that irritate the skin.
Allergy skin tests take place when allergy shots are being considered. Testing may also be necessary for people with potentially serious allergic reactions or asthma.
Are there any risks and precautions?
Although an allergy skin test is generally considered safe, it does have some risk of side effects or complications: These include hives or wheals (swollen, red, itchy bumps on the skin).
Some people have extremely serious allergic reactions called anaphylactic reactions. If a person has had an anaphylactic reaction to an allergen in the past, they may not have an allergy skin test for this substance as the test might provoke a dangerous reaction.
The most serious risk of having a skin prick test is anaphylactic reaction. This reaction is a medical emergency, causing difficulty breathing and a dangerously low blood pressure. However, anaphylactic reactions with skin prick tests are rare and the allergist will be monitoring you closely.
Skin testing may not be performed if you have certain skin conditions, such as severe eczema or atopic dermatitis.
If you are concerned about any symptoms following this test, speak to your doctor. Take the time to be sure you understand all the risks of complications and side effects as well as any precautions you or your doctor can take to avoid them. Be sure your doctor understands all your concerns.
What happens during the test?
There are three different types of skin tests.
The first is called a skin prick test or scratch test.A small amount of substance is pricked or scratched on the skin with a sterile needle. If the area becomes red, itchy, or swells, the allergy skin test is positive. If there is no reaction, the test is negative. This test is usually used to test for allergies to pollen, mould, pet dander, dust mites, and foods.
The second test is called an intradermal test. A small amount of substance is injected into the skin. The intradermal test may be done when the skin prick test is negative but the person is still thought to be allergic to that substance. This test is usually used to identify allergies to bee stings and other insect venom, or penicillin.
The third test is the skin patch test. The substance is placed on a patch and the patch is placed on the skin for 48 hours. After the patch is removed, there will be another appointment 2 days after where the doctor examines the skin again. This test shows whether a person develops contact dermatitis (rash), which is an allergic reaction on the skin due to direct contact with an allergen such as latex, medications, or fragrances.
Allergy skin tests are typically done on the back or the back of the arm, depending on the number of allergens being tested. If a person is being tested for several allergens, a grid may be used to separate the different substances from each other and keep track of them.
A reaction can usually be seen within 15 minutes for the scratch and intradermal tests, while patch tests are examined usually after 48 hours and again at 96 hours. It is best to not take a bath, shower, or sweat excessively while wearing the patch to prevent it from loosening and falling off.
If you have an allergic reaction to any of the skin tests, you may experience some itching, tenderness, and swelling at the test site. These symptoms can be relieved by a cold compress or a steroid cream.
The doctor may choose to do an allergy blood test along with the skin allergy test. This test measures the levels of antibodies in the blood. The levels of antibodies may be elevated if a person is allergic to the substance. A blood test can also be done if a person cannot have a skin test.
How should I prepare for this test?
Before having this test, discuss the advantages, disadvantages, long-term risks, and consequences associated with the test with your doctor. Be sure you fully understand what will happen and are comfortable with your doctor's answers to your questions.
There are no food or drink restrictions before going for an allergy skin test or an allergy blood test.
Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter (non-prescription), and herbal medications that you are taking. Also tell them about any medication allergies and medical conditions that you may have.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist whether you need to stop taking any of your medications before the test. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking some medications before the tests, such as antidepressants or antihistamines that may affect the allergy skin test results. Antidepressants and antihistamines do not have any effect on an allergy blood test.
What can I expect after the test?
If your allergy skin test is positive, you have several options to prevent an allergic reaction from occurring again. Some people choose to undergo desensitization, where small amounts of the allergen are gradually introduced to the body so that the person develops immunity to the allergen.
If an allergic reaction develops, antihistamines can be used to relieve symptoms.
Your allergist may also discuss helpful strategies to help you avoid or minimize exposure to allergens.
Results
The skin prick test and intradermal test can be read within about 15 minutes and the allergist can tell you the result during that same visit. The skin patch test requires you to return to your doctor's office at the 2 day (48 hours) and 4 day (96 hours) mark. At that point, your doctor can tell you the results. Blood samples are sent to a lab and may take about a week before results are available.
The accuracy of the skin test can vary. It is possible that you may react differently to the same substance at different times or react positively to the test yet not in everyday life.
All material copyright MediResource Inc. 1996 – 2024. Terms and conditions of use. The contents herein are for informational purposes only. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Source: www.medbroadcast.com/procedure/getprocedure/Allergy-Skin-Test